💵 Expenses Page
“Track every cost — from restocking to rent, logistics, and beyond.”
🎯 Purpose of This Page
The Expenses Page is designed to help you record and manage any cost that doesn't directly come from a purchase bill or product sale.
You use it to:
- Record operating costs (rent, utilities, salaries)
- Track spending unrelated to stock (e.g., equipment repair)
- Add supplier or customer-linked expenses
- Maintain transparency in clinic, store, or company spending
- Export expense records for accounting or audit
✅ This page works like a simplified ledger of outflows — every money-out event that matters.
👥 Who Uses This Page?
- Finance staff recording bills or payment vouchers
- Store officers logging shipping fees or losses
- Procurement staff recording vendor charges
- Hospital administrators tracking patient-related expenses
- Clinic managers logging salary, fuel, or repair expenses
🧾 What You Can Record
| Expense Type | Example Entries |
|---|---|
| 📦 Shipping | Courier fee for emergency delivery from supplier |
| 🧰 Maintenance | Cost to repair faulty storage fridge |
| 🏠 Rent | Monthly space rental fee for storage unit |
| ⚡ Utilities | Electricity or internet payment |
| 👥 Salaries | Payments to temp workers or contracted staff |
| 📃 Other | Donation payouts, insurance fees, etc. |
🛠️ What You Can Do On This Page
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔎 Search Bar | Search expenses by keyword (e.g., “Internet”) |
| 📅 Date Filters | Filter by “Today,” “Last Week,” “This Month,” etc. |
| 👤 Link to Customer | Optional – tag an expense to a specific customer (e.g., refunds) |
| 🧾 Description Field | Clearly explain the reason for expense |
| 💵 Amount Field | Record exact value spent |
| 🧑 User Tagging | System logs which user recorded the expense |
| 📄 Print / Export | Download or print the expense sheet |
🧰 Example Workflow: Logistics Cost
- You pay $150 for express shipping of emergency insulin.
- Open Expenses Page
- Click Add New
- Enter:
- Description: “Express shipping – insulin”
- Amount: 150
- Date: Today
- Save record
- ✅ Print or export later for reimbursement/audit
📈 Example: Monthly Report
The finance team wants to know how much you’ve spent this month outside of purchases.
- Filter: This Month
- View the expense list and total at the bottom
- Click Export CSV
- Submit file with monthly finance report
📬 Link to a Customer (Optional)
In scenarios where you’re refunding a customer or paying something on their behalf:
- Use the Customer field to tag the person
✅ This helps track all spend related to a single customer.
🧠 Useful for:
- Refunds
- Charity support
- Donated goods or grants
🖨️ Export & Print
At any point, you can:
- Export by month, user, or keyword
- Print a receipt or voucher-like sheet
- Store hard copies or attach to physical finance files
🧠 Best Practices
- Add clear, specific descriptions
- Encourage staff to tag users so actions are traceable
- Review expenses weekly or monthly
- Use filters to isolate by customer, date, or keyword
- Use the exported file as part of your bookkeeping or audit trail
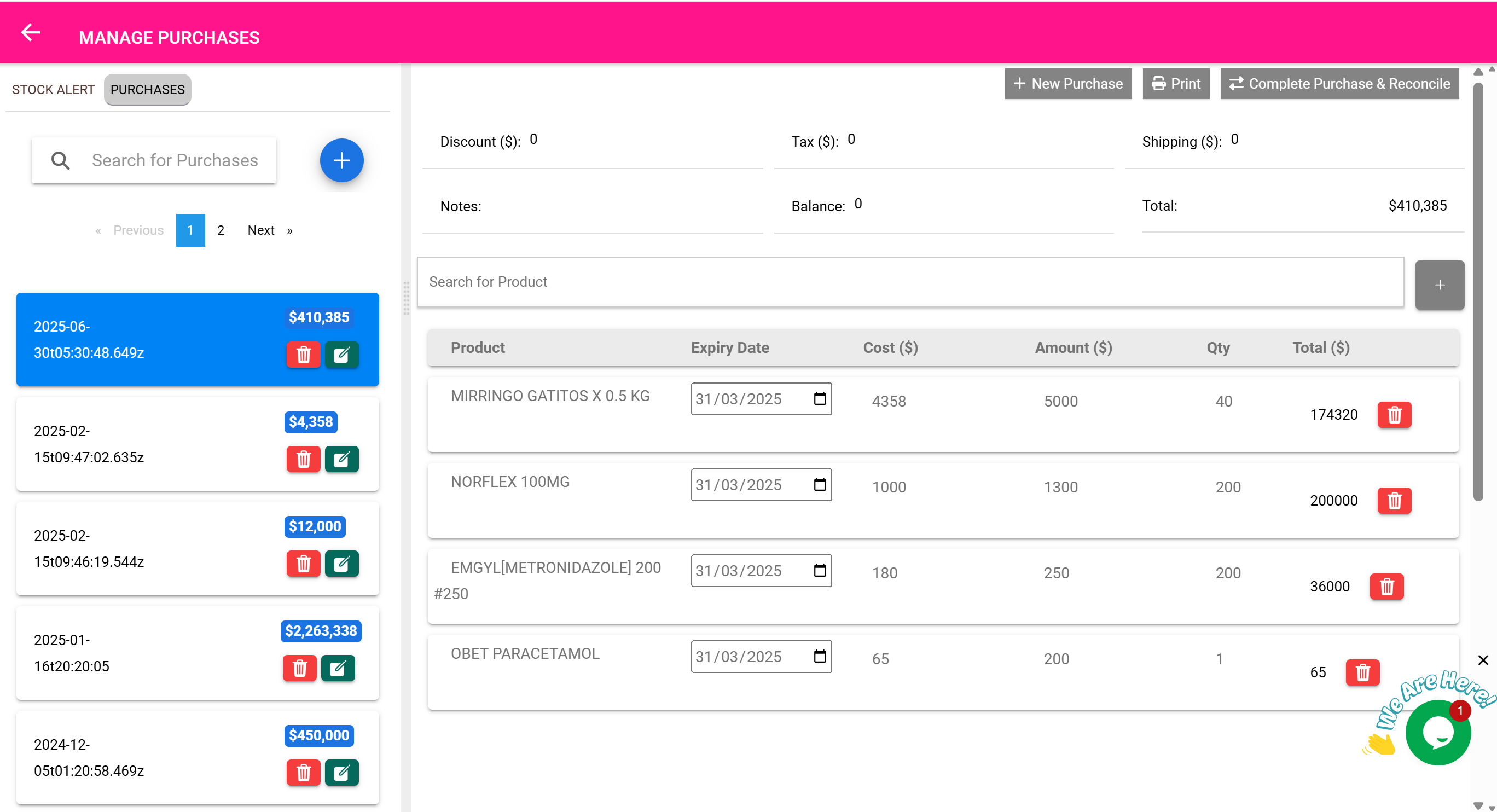
🔁 Purchases Are Automatically Tracked as Expenses
Every time you complete a purchase order (via the Purchases Page), the system automatically logs it as an expense entry.
This means:
- You don’t need to manually add the cost of purchased items to the Expenses Page.
- The cost of goods purchased (including tax and shipping) is captured under supplier-linked expense records.
- These appear in your expense exports and totals — helping you track both inventory costs and operating costs from a single place.
🧠 Example: Automatic Purchase Expense
You purchase $500 worth of antibiotics from “ABC Pharma” and mark the purchase as completed.
A new expense record is automatically created in the system. It includes:
- Supplier: ABC Pharma
- Amount: $500
- Description: “Purchase – Antibiotics”
- Date and user who performed the transaction
✅ It becomes visible in financial summaries and exports from the Expenses Page.
📌 Why This Matters
- Ensures no cost is missed when calculating operational expenditure
- Gives a complete financial overview — from purchases to utilities, logistics, and rent
- Helps the finance department reconcile spending against inventory movement